Research Areas
Biomaterials
Biomaterials related research carried out in the Center for Biomedical Engineering facilities or involving Biomedical Engineering graduate students spans a range of activities. Topical areas include:
- Anti-microbial polymer development;
- Tissue engineering and tissue models;
- Control of cell-surface interactions;
- Development of nanoparticles and microparticles for therapeutic or diagnostic applications;
- Development and applications of model biological membranes.
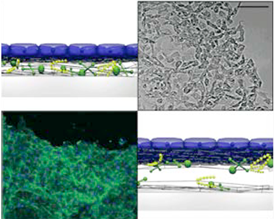
Biocompatible thin-film deposition to direct
mammalian cell adhesion and release
(from H.E. Canavan, et al.)
Instrumentation and Bioanalytical Methods
An essential element of interdisciplinary research is the development of new measurement techniques and tools. At the Center for Biomedical Engineering, these activities contribute to our emphasis area in Instrumentation and Bioanalytical Methods. Topical areas include:
- Novel flow-based analysis methods and instruments, including large particle analysis, high- throughput and large-volume analysis, and nanoparticle-based assays;
- New sensing strategies based on biomolecular computing;
- Enzymatic biosensor development and fuel-cell technologies
- Optical sensing strategies including fluorescence lifetime or intensity-based methods to study biomolecular interactions and chemical microenvironments in complex biological settings
- Biomolecular separation strategies based on new fluidic architectures
- Raman and surface-enhanced Raman based sensing and analysis
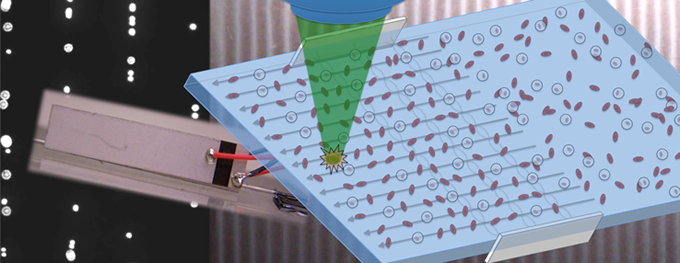
Instrumentation for high-throughput parallel flow cytometry
(from S. Graves, A. Shreve, et al.)
Computation and Modeling of Biological Systems
Development of quantitative models for understanding biological systems applies engineering-based methods to problems in:
- Tumor biology
- Signal processing
- Use of biological materials for computations
- Mutli-scale temporal and spatial processes
Many of The Center for Biomedical Engineering's activities in this area involve partnerships with other organizations such as the Spatiotemporal Modeling Center, the Computer Science Department, the UNM Cancer Center, Sandia National Laboratories, and Los Alamos National Laboratory.
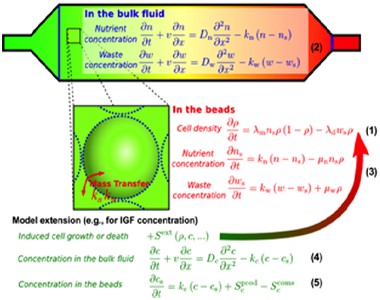
Modeling transport in 3D cell culture system
(V. Cristini with J. Freyer, A. Shreve)
